Artificial intelligence (AI) and cryptocurrency/blockchain have each revolutionized technology – but what happens when they meet? As AI and crypto collide, they create powerful synergies and new ethical challenges. Imagine autonomous trading agents negotiating on blockchains, or decentralized AI marketplaces exchanging smart contracts. These possibilities spark both excitement and concern. On one hand, blockchain’s immutable ledger can increase trust in AI systems. On the other, AI-driven crypto bots can exploit markets and privacy. This blog explores where AI and crypto intersect, examining the ethical landscape, spotlighting projects like SingularityNET, Fetch.ai, and Numerai, and envisioning the future of AI-powered crypto trading.
AI and Blockchain: Complementary Technologies
AI excels at learning from data and making predictions, while blockchain offers a secure, transparent data infrastructure. In fact, blockchain’s decentralized ledgers can address many AI ethics issues business.com. For example, immutable records on a blockchain could log AI decision processes, making them traceable and auditable meegle.com. Researchers note that blockchain can “verify the provenance of AI training data”, ensuring inputs are unbiased and ethically sourced. In practice, blockchain’s tamper-proof database can protect sensitive personal or behavioral data that feed AI models. As one infographic explains, AI recommendation engines on platforms like Amazon risk privacy breaches (e.g. Cambridge Analytica). By storing user data across a decentralized network, blockchain can keep that data secure even if some servers are hacked aibusiness.com.
In synergy, AI and blockchain help each other. AI brings “intuitive self-learning algorithms”, while blockchain provides infrastructure “not controlled by any particular person” aibusiness.com. AI can optimize blockchain (e.g. intelligent scaling, fraud detection) and automate processes in smart contracts. Conversely, blockchain can enforce transparency in AI: an immutable ledger lets anyone audit an AI’s decisions. According to Nir Kshetri, blockchain’s contributions include “enhancing data security and privacy” and enabling decentralized AI development with stronger ethical governance researchgate.net. In short, combining the two can create systems that are both intelligent and trustworthy meegle.com.
Key Ethical Challenges at the Intersection
While the fusion of AI and crypto offers promise, it also raises novel ethical dilemmas. The following key issues emerge when AI meets blockchain:

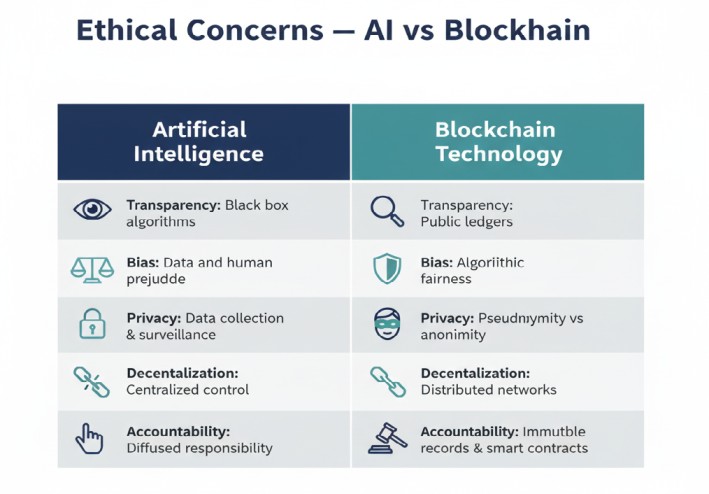
- Data Privacy vs Transparency: AI often requires massive data (from social media, sensors, markets), raising privacy concerns. Blockchain’s transparency can conflict with privacy. Who sees the data that trains or is generated by AI? If AI models are built on on-chain data, do we risk exposing personal information? As analysts warn, “AI’s reliance on vast amounts of data” creates data exploitation risks coinprwire.com. For instance, AI trading bots ingest real-time financial and personal trading data, so ensuring consent and anonymization is critical.
- Bias and Fairness: AI can inadvertently learn biases present in data. On an immutable blockchain, biased decision logs could persist unchecked. However, blockchain can mitigate bias by certifying data sources. As one guide notes, using blockchain to “verify the provenance of AI training data” can help keep it free of bias meegle.com. Still, if on-chain AI models favor certain assets or users, that bias may be hard to correct. Preventing algorithmic discrimination (e.g. AI bots giving unfair access) is an open challenge coinprwire.com.
- Accountability and Transparency: AI systems are often “black boxes” with opaque logic. When a self-learning AI executes a smart contract or trades cryptocurrency, who is responsible for mistakes? The lack of transparency in decision-making can “erode trust” onesafe.io. Regulators are asking tough questions: how do we audit an AI’s on-chain actions? The need for explainable AI is as strong as ever; blockchain can help by recording AI decisions, but someone must still answer for outcomes coinprwire.com.
- Market Manipulation and Fair Play: AI-powered trading brings speed and efficiency – but also risk. High-frequency AI bots can amplify flash crashes or be programmed for pump-and-dump schemes. Indeed, experts warn that automated, millisecond trades can give large funds an unfair edge. Examples include “front-running” where an AI detects pending orders and jumps ahead of them coinprwire.com. These practices undermine market fairness, sparking calls for oversight. As one commentator puts it, the AI advantage may violate fair-play principles unless managed carefully onesafe.io.
- Regulation and Governance: Neither AI nor crypto has complete regulatory clarity. Combining them complicates compliance. Policymakers grapple with questions like: Should AI crypto bots be regulated like financial advisers? How to ensure on-chain AI adheres to ethical guidelines? Many argue for new frameworks and auditing mechanisms so that AI-crypto systems remain transparent and accountable coinprwire.com. International cooperation will be key, as these technologies transcend borders.
- Environmental Impact: Training AI models and mining cryptocurrencies both consume significant energy. This dual footprint raises social responsibility issues. Ethically, projects must consider green computing and consensus methods. Some blockchain-AI projects (e.g. those focusing on IoT agents) are actively seeking low-energy solutions. As sustainability becomes a priority, developers must weigh compute costs against benefits.
In sum, AI-blockchain integration demands new ethical standards. Transparency, fairness, and security must be engineered from the start. Experts encourage practices like open-source AI models, data audits, and immutable logging to mitigate risks. For example, using blockchain to provide “traceable and auditable” AI decision processes is one suggested benefit meegle.com. In this way, the immutable ledger helps enforce responsible AI use.
Spotlight: Decentralized AI-Crypto Projects
Several cutting-edge projects illustrate how AI and crypto intertwine:
| Project | Focus | Token | Ethical Angle |
|---|---|---|---|
| SingularityNET | Decentralized AI marketplace | AGIX | Democratizes AI access diadata.org |
| Fetch.ai | Autonomous agent economy | FET | Open “agentic” marketplace for AI tasks fetch.ai |
| Numerai | AI-driven hedge fund tournament | NMR | Crowdsourced trading; encrypted data; model staking numer.ai |
| Cortex | On-chain AI computation | CTXC | Enables on-chain ML models; open ecosystem cortexlabs.ai |
| Ocean Protocol | Decentralized data exchange for AI | OCEAN | Secure, tokenized data sharing |
- SingularityNET (AGIX): “the world’s first decentralized AI network” diadata.org. SingularityNET runs an AI service marketplace on blockchain: anyone can publish or consume AI algorithms at scale. By tokenizing AI services, it aims to break AI monopolies. Its vision of “decentralized AI” focuses on fairness and open access diadata.org. In their Beneficial AI Network, SingularityNET explicitly encourages AI applications that address social challenges ethically diadata.org.
- Fetch.ai (FET): Fetch.ai builds a platform for autonomous software agents to buy/sell data and services in a decentralized economy. According to its docs, Fetch.ai is creating “an AI empowered agent based decentralized digital economy” fetch.ai. In practice, that means AI agents can automatically trade on behalf of users (e.g. smart IoT devices optimizing energy use). Fetch.ai’s governance and token model aim to keep this system open: any agent uses FET tokens for micropayments, creating an “Agentic AI” ecosystem. Notably, Fetch.ai led the creation of the Artificial Superintelligence Alliance (ASI) with SingularityNET (see below).
- Numerai (NMR): Numerai is a novel crypto-based hedge fund powered by AI. Data scientists worldwide build machine learning models on Numerai’s encrypted financial data. They then stake NMR tokens on their predictions. If a model is accurate, its creator earns more NMR; if wrong, staked tokens are lost numer.ai. This mechanism aligns incentives: it crowd-sources AI to improve the fund’s performance. Numerai’s approach preserves data privacy (the input data is obfuscated) while fostering a transparent, decentralized research community. It’s an example of crypto incentivizing ethical collaboration in AI.
- Cortex (CTXC): Cortex’s blockchain is built specifically to run AI models on-chain. It provides a machine learning inference engine so that smart contracts can call AI APIs natively. Cortex’s mission is to “decentralize AI research” cortexlabs.ai by rewarding researchers to upload models to the blockchain. In an open ecosystem, the best models compete, theoretically reducing bias over time. Cortex demonstrates how blockchain can democratize access to AI intelligence for any DApp.
- Ocean Protocol (OCEAN): Ocean is a decentralized data marketplace enabling individuals and organizations to share and monetize AI data. Ethically, this supports data sovereignty: data owners control access via smart contracts. AI researchers get broader, permissioned datasets, potentially improving model quality and fairness. While not an AI engine itself, Ocean’s role is critical at this intersection by solving the data availability problem for AI on blockchain.
Some of these projects even united: in April 2025, Fetch.ai and SingularityNET (with Ocean Protocol) formed the Artificial Superintelligence Alliance (ASI) osl.com. This merger aimed to create a decentralized counterforce to Big Tech’s AI. The ASI alliance consolidated the partners’ tokens (now a single $ASI token) and shared their resources osl.com. Importantly, the alliance publicly committed to ethical AI practices. Their vision stresses open, democratic AI development “beneficial to all”, emphasizing transparency and accountability osl.com. By pooling data sharing and decentralized models, ASI showcases how collaboration in AI and crypto can promote inclusivity – setting a real-world standard for ethical innovation.
AI and Crypto Trading: The Road Ahead
AI is already transforming crypto markets, and this trend will accelerate. Machine learning models analyze price trends, news sentiment, and on-chain data to generate trading signals. High-frequency trading bots powered by AI can execute strategies with minimal human intervention. This future of AI in crypto trading offers huge potential: better risk management, liquidity, and 24/7 market monitoring. However, the ethical stakes rise accordingly.

Experts warn of an “ethical quagmire” in AI-powered trading onesafe.io. On the upside, AI can help detect fraud or irregular patterns (using explainable AI on blockchain data). On the downside, it can also produce unequal advantages and market anomalies. As one analysis notes, AI’s predictive power lets some “hop on emerging trends” far quicker than others onesafe.io. Those without access to sophisticated AI tools (e.g. many retail investors) could be left at a disadvantage, undermining the fairness of free markets coinprwire.com.
Safety nets and oversight are crucial. Some suggest mixed human-AI approaches: for instance, human traders could supervise AI decisions to ensure they align with ethical norms onesafe.io. Real-time monitoring and alerts might also catch suspicious trades as they happen. Others advocate industry standards: auditing AI trading algorithms and disclosing model behaviors. Indeed, regulatory bodies are already discussing AI-specific rules for financial markets coinprwire.com. The consensus is that unchecked AI could erode market integrity, so proactive governance is needed coinprwire.com.
The bottom line: the future of AI in crypto is bright but not without hazards. As technologies evolve, developers and regulators must balance innovation with ethical guardrails. Traders and investors should demand transparency in AI tools they use. Educators and platforms can promote ethical AI guidelines (e.g., fairness, non-manipulation). By fostering responsible AI integration today, the crypto industry can reap AI’s benefits – increased efficiency and security – without sacrificing trust.
Conclusion
The intersection of AI and crypto presents a thought-provoking frontier. On one hand, combining these technologies can solve each other’s weaknesses – blockchain securing AI data, and AI strengthening blockchain applications. On the other, it creates new ethical puzzles: how do we ensure fairness, prevent exploitation, and maintain privacy in an automated, decentralized world? The examples of SingularityNET, Fetch.ai, Numerai and others show that conscious design and community governance can steer this synergy toward positive ends.
As readers, consider this: how would you feel about an AI setting your investment strategy on-chain? What safeguards would you demand? Share your thoughts below! If you found these insights useful, consider subscribing for more on AI and blockchain, or exploring ethical frameworks in emerging tech. Together, we can shape an innovative future where AI and crypto serve everyone responsibly.
Don’t let the learning stop here! Dive into our other articles (Blockchain, Geopolitics & Crypto, DeFi, Smart Contracts Future of Crypto Currency) and keep exploring the future of finance.




Pingback: Crypto Bridge: How to Transfer Assets Between Blockchains - tokensbuzz.com
Pingback: Bitcoin Halving Explained: What It Means for Investors (2025) - tokensbuzz.com